Deploy dbt projects to Astro
Astro supports a range of options when it comes to adding your dbt project to your Deployment. To orchestrate dbt jobs with Apache Airflow, you first need to deploy your dbt project to Astro along with your dags and the rest of your Airflow code.
This guide includes information on the different options your team has for deploying dbt code to Apache Airflow and Astro. Your team can choose the option that best fits your team’s software development lifecycle.
For more information and recommendations on using dbt with Apache Airflow and Astro, see Orchestrate dbt Core jobs with Airflow and Cosmos.
Repository strategy
Depending on your organization’s software development lifecycle, there are three ways you can organize your dbt project relative to your Astro project:
- In the same Git repository and directory as your Astro project.
- In the same Git repository but in a separate directory.
- In a separate Git repository.
Astro supports all three methods, but Astronomer recommends having your dbt project in the same Git repository as your Astro project, but in a different directory. Then, you can use dbt deploys to independently deploy dbt code to Astro from your dbt directory without needing to deploy either a full Astro project image or your dags. This strategy allows your team maintaining dbt to work independently from your team managing Airflow dags, but team members can all see shared code in a single Git repository.
You can see additional recommendations for Astro repository strategy, in the Repo strategy best practices guide.
Feature overview
Astro supports two basic dbt code deploy strategies. You can:
- Include dbt code in your Astro project: Make dbt code directly available in the Docker image powered by Astro Runtime that contains your Astro project. This approach works best for small teams just starting to integrate dbt code in Astro.
- Use dbt Deploys: Independently deploy bundles of dbt code directly to Astro, outside the context of your Astro project and Docker image. Astronomer recommends this approach for teams who have dbt code in a dedicated directory or Git repository.
Option 1: Include dbt code in your Astro project
The most direct way to set up dbt on Astro is by including dbt code in your full image. To accomplish this, Astronomer recommends adding the directory /dbt to the top level of your Astro project and including individual dbt projects inside this directory.
Finally, to push your new dbt code to your Deployment, perform a deploy with the Astro CLI by running:
While this is the quickest way to get dbt code in your Deployment, there can be drawbacks if your team makes more frequent changes to dbt code or uses more advanced CI/CD. These include:
- Slower build times when changing only dbt code.
- dbt code must live in the same repository and directory as your Astro project.
- Multiple teams developing Airflow and dbt separately must re-deploy the entire Astro project for each iteration.
If these downsides become applicable to your team, try Option 2.
Option 2: Use dbt Deploys to independently ship dbt code
dbt Deploys allow you to easily deploy your dbt project to Astro without needing complex processes to incorporate your two sets of code. When you use a dbt Deploy, Astro bundles all files in your dbt project and pushes them to Astro, where they are mounted on your Airflow containers so that your dags can access them. This allows you to deploy dbt code without requiring you to use a full Astro image deploy.
Prerequisites
- An Astro Deployment
- An Astro project. Astronomer supports both dbt Cloud and dbt Core.
- A dbt project
- The Astro CLI v1.28 or greater
Step 1: (Optional) Deploy your full Astro image
In order to first deploy a dbt project to Astro, Astronomer recommends that you have an Astro project already running on your Deployment with dags that need to read from dbt. That way, your dbt project will be read and used when you deploy it.
If you are using a new Deployment, first deploy your Astro project with the Astro CLI by running:
Step 2: Deploy your dbt project
Next, navigate to the directory of your dbt project. This directory should include the dbt_project.yml file, as in the case of the Classic dbt Jaffle Shop in the following example:
From the CLI, run the following command to deploy your dbt project. The command prompts you to choose the Deployment that you want to deploy your dbt project to.
By default, astro dbt deploy attaches the dbt code to the default path of /usr/local/airflow/dbt/<dbt-project-name>.
See astro dbt deploy for more information about this command.
If your dbt code is accessed at a different path or folder than the default path, specify a custom mount path with the following flag:
Congratulations, you’ve added your dbt code to your Deployment! Check the Astro UI to see more information about your dbt Deploy.
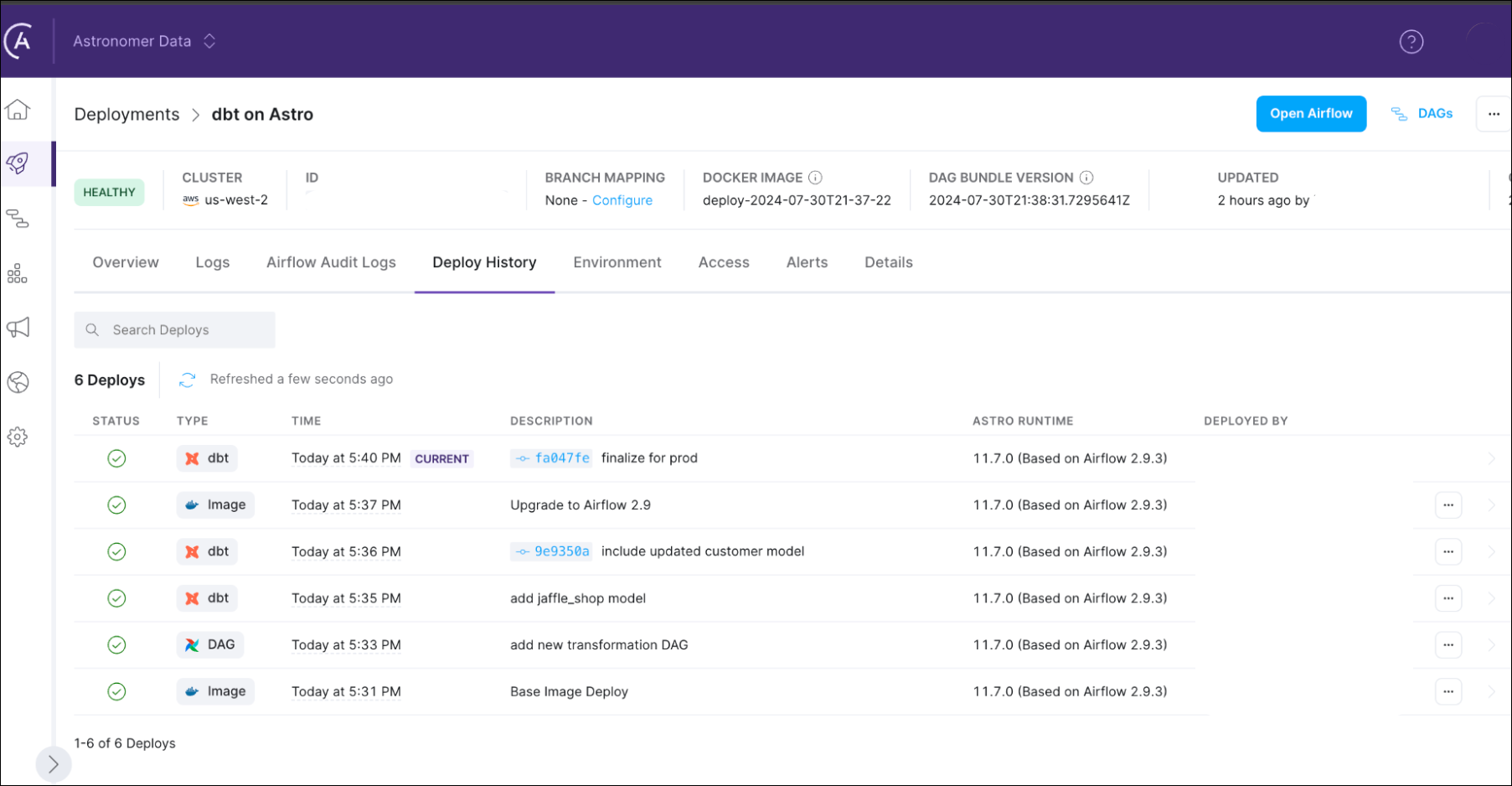
Delete your dbt project
If you want to remove dbt code from your deployment, you can also delete the dbt project from the Airflow environments where you deployed it. This command does not delete your dbt project source files. It only removes your project from the Airflow containers where it was mounted. When you run this command, you will be prompted to choose the Deployment from which you want to remove the project.
See astro dbt delete for more information about this command.