Orchestrate Ray jobs with Apache Airflow®
Ray is an open-source framework for scaling Python applications, particularly for machine learning and AI workloads where it provides the layer for parallel processing and distributed computing. Many large language models (LLMs) are trained using Ray, including OpenAI’s GPT models.
The Ray provider package for Apache Airflow® allows you to interact with Ray from your Airflow Dags. This tutorial demonstrates how to use the Ray provider package to orchestrate a simple Ray job with Airflow in an existing Ray cluster. For more in-depth information, see the Ray provider documentation.
For instructions on how to run Ray jobs on the Anyscale platform with Airflow, see the Orchestrate Ray jobs on Anyscale with Apache Airflow® tutorial.
This tutorial shows a simple implementation of the Ray provider package. For a more complex example, see the Processing User Feedback: an LLM-fine-tuning reference architecture with Ray on Anyscale reference architecture.
Time to complete
This tutorial takes approximately 30 minutes to complete.
Assumed knowledge
To get the most out of this tutorial, make sure you have an understanding of:
- Ray basics. See the Getting Started section of the Ray documentation.
- Airflow decorators. See Airflow decorators.
Prerequisites
- The Astro CLI.
- Optional: A pre-existing Ray cluster. This tutorial shows how to spin up a local Ray cluster using Docker. To connect to your existing Ray cluster, modify the connection defined in Step 2.
The Ray provider package can also create a Ray cluster for you in an existing Kubernetes cluster. For more information, see the Ray provider package documentation. Note that you need a Kubernetes cluster with a pre-configured LoadBalancer service to use the Ray provider package.
Step 1: Configure your Astro project
Use the Astro CLI to create and run an Airflow project on your local machine.
-
Create a new Astro project:
-
In the requirements.txt file, add the Ray provider.
-
(Optional). If you don’t have a pre-existing Ray cluster, you can spin up a local Ray cluster alongside your local Astro project by using a
docker-compose.override.ymlfile. Create a new file in your project’s root directory calleddocker-compose.override.ymland add the following: -
In your
.envfile, specify your Ray cluster address. Modify this address if you are using a pre-existing Ray cluster. -
Run the following command to start your Astro project:
Step 2: Configure a Ray connection
For Astro customers, Astronomer recommends using the Astro Environment Manager to store connections in an Astro-managed secrets backend. These connections can be shared across multiple deployed and local Airflow environments. See Manage Astro connections in branch-based deploy workflows.
-
In the Airflow UI, go to Admin -> Connections and click +.
-
Create a new connection and choose the
Rayconnection type. If you used thedocker-compose.override.ymlfile to spin up a local Ray cluster, use the information below. If you are connecting to your existing Ray cluster, you will need to modify your values accordingly.- Connection ID:
ray_conn - Host:
ray-head - Port:
8265 - Extra Fields:
ray_dashboard_url:"http://ray-head:8265"disable_job_log_to_stdout:false
- Connection ID:
-
Click Save.
If you are connecting to a Ray cluster running on a cloud provider, you need to provide the .kubeconfig file of the Kubernetes cluster where the Ray cluster is running as Kube config (JSON format), as well as valid Cloud credentials as environment variables.
Step 3: Write a Dag to orchestrate Ray jobs
-
Create a new file in your
dagsdirectory calledray_tutorial.py. -
Copy and paste the code below into the file:
Taskflow
Traditional
This is a simple Dag comprised of two tasks:
- The
generate_datatask randomly generates a list of 10 integers. - The
get_mean_squared_valuetask submits a Ray job on Anyscale to calculate the mean squared value of the list of integers.
-
(Optional). If you are using the traditional syntax with the SubmitRayJob operator, you need to provide the Python code to run in the Ray job as a script. Create a new file in your
dagsdirectory calledray_script.pyand add the following code:
Step 4: Run the Dag
-
In the Airflow UI, click the play button to manually run your Dag.
-
After the Dag runs successfully, check go to your Ray dashboard to see the job submitted by Airflow.
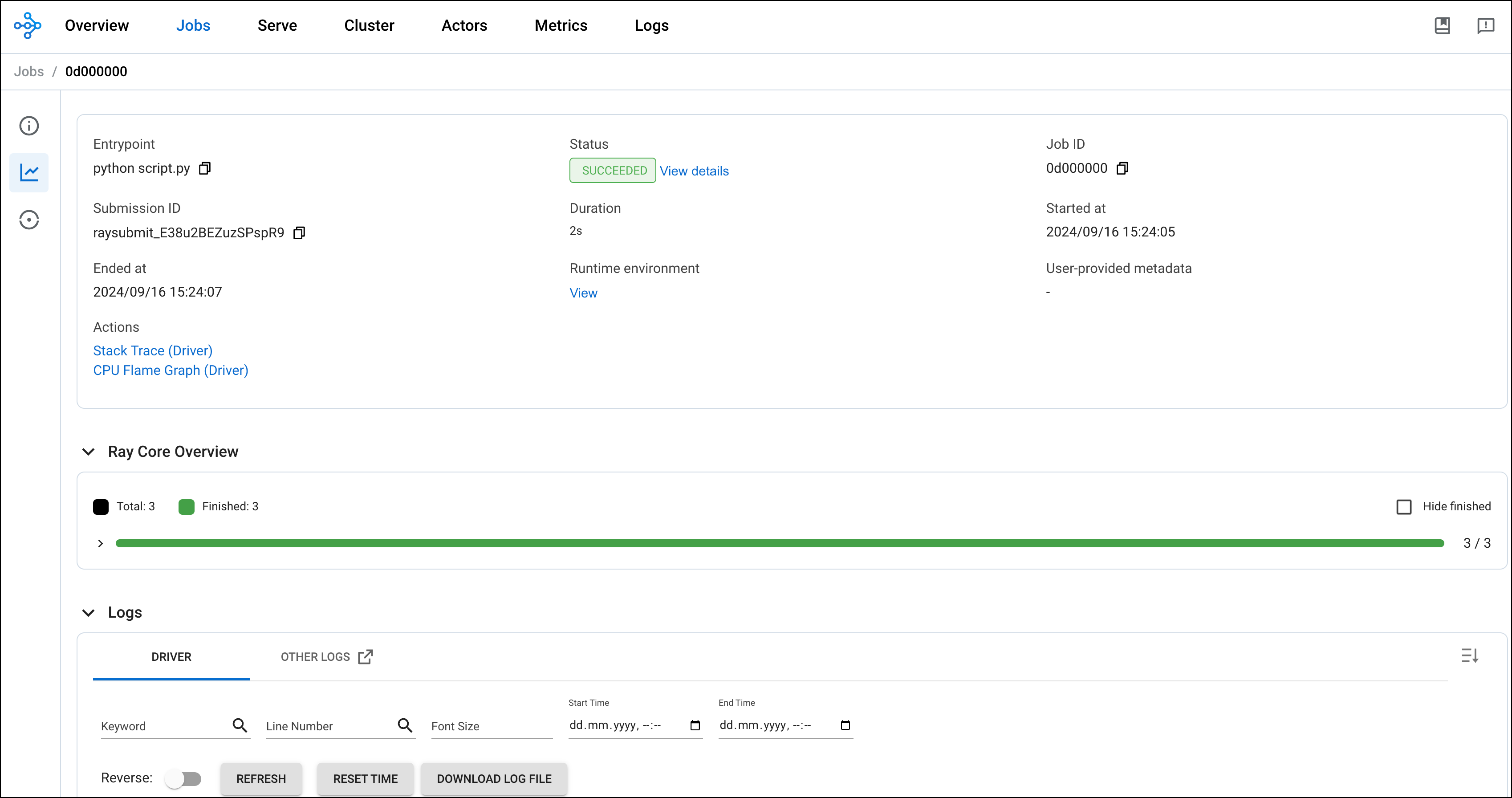
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve run a Ray job using Apache Airflow. You can now use the Ray provider package to orchestrate more complex Ray jobs, see Processing User Feedback: an LLM-fine-tuning reference architecture with Ray on Anyscale for an example.